- Details
- Category: Raspberry
- Hits: 670
Recently I had to build a Linux kernel on my Raspberry Pi5 and detected the system became quite hot even with an original active cooler. That's the way I monitored the CPU usage and fan speed.
Read more: How to monitor CPU usage and cooling on a Raspberry
- Details
- Category: Raspberry
- Hits: 21495
I recently got a compute module 4 (CM4) donated to add support for NVMe in raspiBackup (See here for details). I'm used to use a Raspberry but never used a CM4 before so I had to ramp up on CM4 first. The following page describes how I managed to get a RaspbianOS (Buster) up and running on the CM4 and to boot from NVMe.
My CM4 specs: 1GB main memory, 32GB eMMC and 128GB NVMe from Hynix, no WiFi and a Waveshare Mini Base Board A (CM4-IO-BASE-A)
Parts
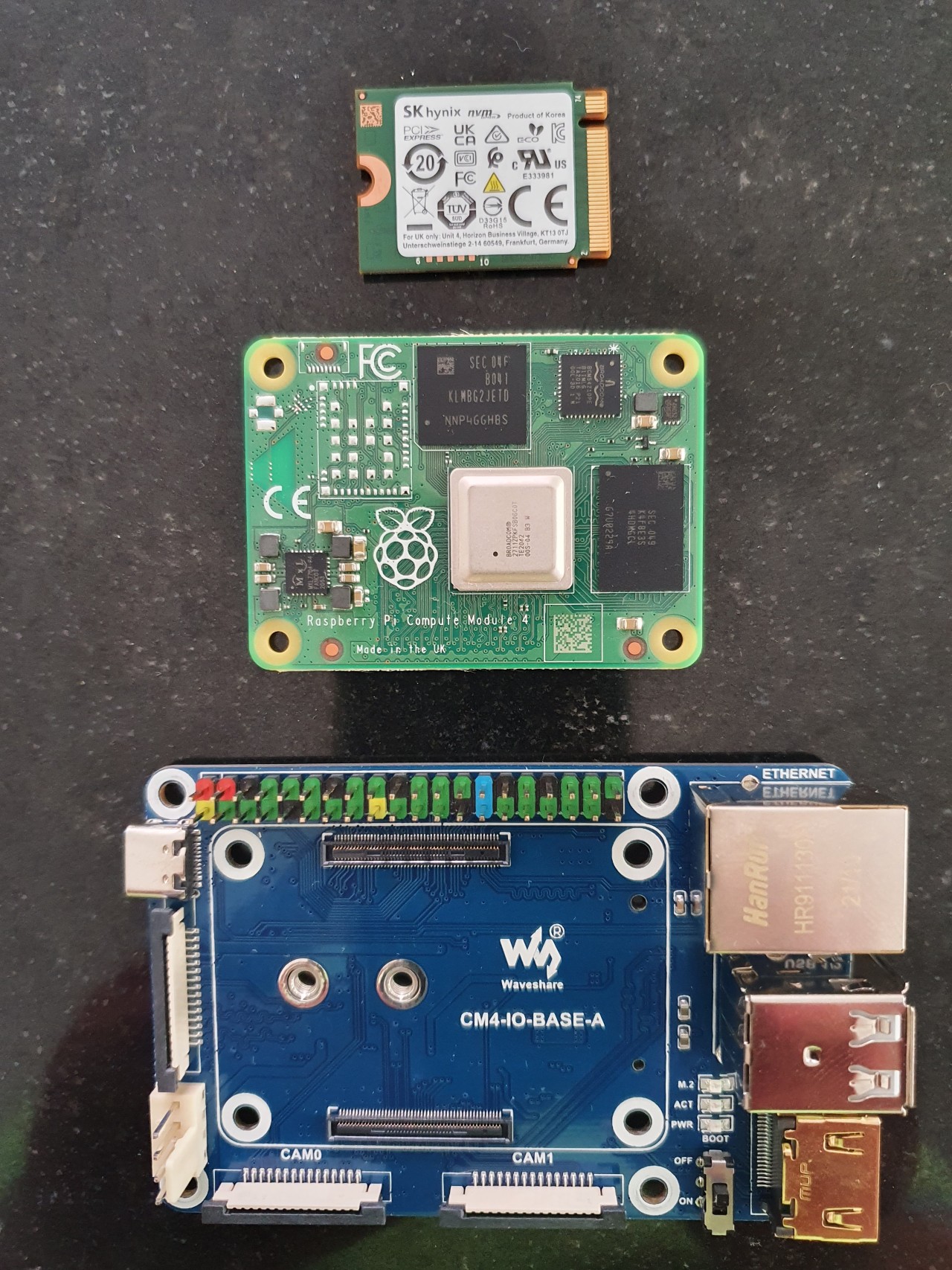

Hynix NVMe, CM4 and Waveshare Mini Base Board A (from top to bottom)
Parts assembled
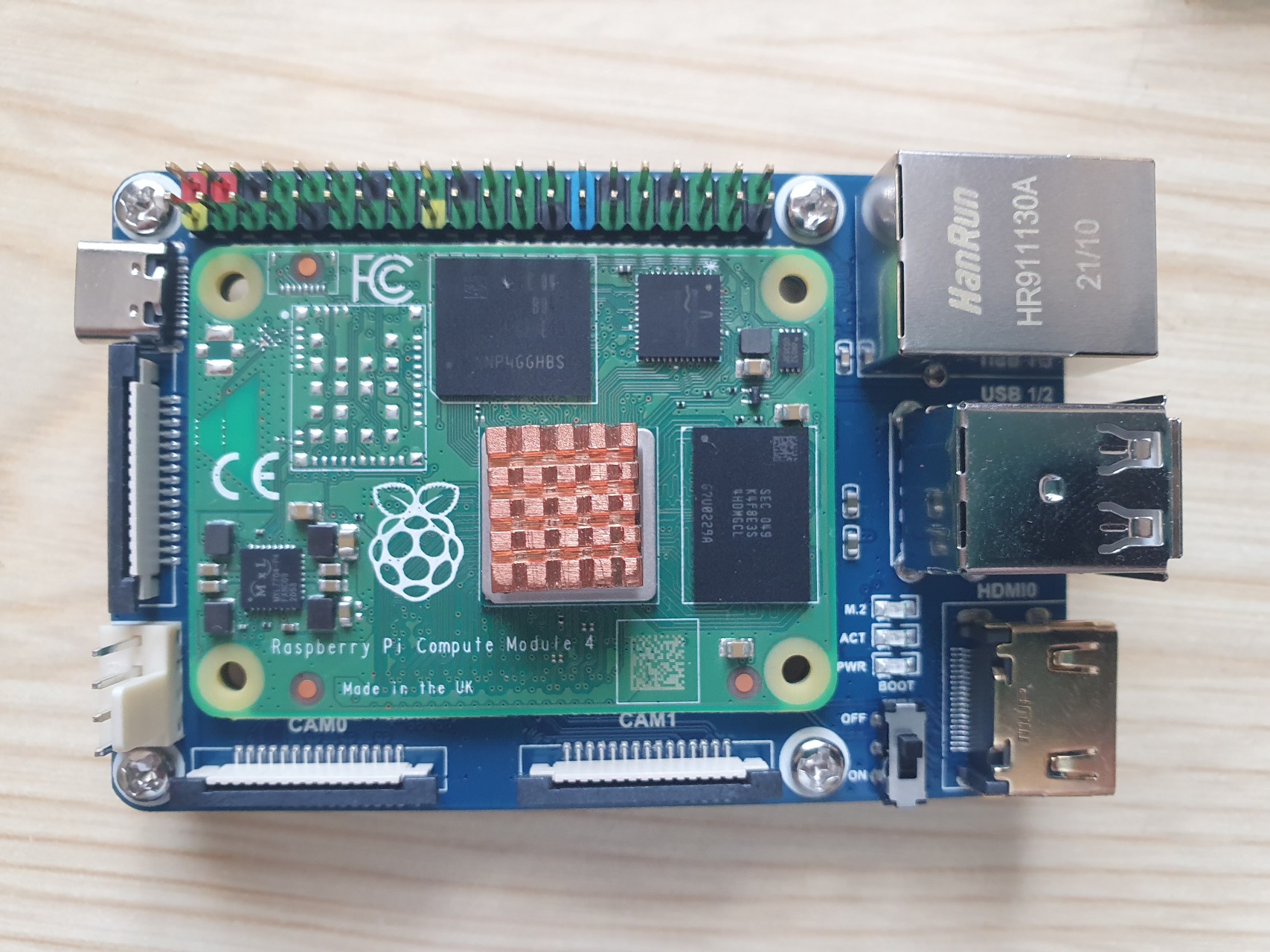
Read more: Raspberry Compute Module 4 (CM4) setup guide on eMMC and NVMe
- Details
- Category: Raspberry
-
Also available:

- Hits: 37732
A lot of people are interested in a Raspberry Pi and want to get some idea about the operating system running on Pi without the need to buy a Pi first. I actually searched for a convenient way to test a backup script called raspiBackup I wrote for the Raspberry Pi. A nice way to evaluate Raspbian or to run any tests is to use QEMU to emulate the Raspberry Pi. Note that special Pi hardware like GPIO et al cannot be simulated. It's just the processor which is simulated. You need a Raspbian image and a system with Linux or Windows. Today I configured my system to run a Pi in QEMU and in the following article I explain step by step how I installed and configured QEMU on my Debian based Linux. The image has a networking connection right after startup and will use the existing host network connection with NAT. Finally a script is provided which executes the steps described and simplifies the image creation process.
- Details
- Category: Raspberry
-
Also available:

- Hits: 1848
btrfs has some nice features. That's why it makes sense to convert the root filesystem of a Raspberry running RaspbianOS from ext4 to btrfs.
Note: The following instructions require basic Linux knowledge because it's just a memory aid for me and the instructions are not very detailed.
Read more: Convert a rootfilesystem of a Raspberry from ext4 to btrfs
- Details
- Category: Raspberry
- Hits: 3583
Just call
curl https://download.argon40.com/argon1.sh | bash
If you run Ubuntu just call
cd /tmp/
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/meuter/argon-one-case-ubuntu-20.04/master/argon1.sh
chmod a+x argon1.sh
sudo ./argon1.sh
Read more: How to install ARGON ONE PI4 Power buttons & fan control
- Details
- Category: Raspberry
-
Also available:

- Hits: 3772
Starting with Bookworm /boot/cmdline.txt was maoved to /boot/firmware/cmdline.txt. Therefore rpi-clone can unfortunately no longer update the UUID of the clone and the clone no longer starts. Details are described here on github.
Read more: rpi-clone doesn't create a bootable clone any more on Bookworm
- Details
- Category: Raspberry
-
Also available:

- Hits: 3814
PiShrink is a useful tool to compress backups created with win32diskimager and other windows tools as a full backup to reduce them to a minimum size.
It's a hack and works a lot of time. Unfortunatey there are a lot of situations you get an ugly error message which are created because of missing checks in the code.
- Details
- Category: Raspberry
-
Also available:

- Hits: 5669
Following page describes how to use a ZTE ML190 USB drive to receive SMS and forward them to another mobile phone number. But you can also send the SMS in an eMail or do other stuff. You can control any devices at home, i.e. turn on or turn off some device, open and close your garage and much more.
Update 5/2/2023
gammu requires Pyhon2 and will not be migrated to Python3. Therefore I now use smstools. Sample event handler smsevent includes a lot of sample code which only has to be adapted to the specific requirements.
Read more: Use ZTE ML190 USB pen drive to create a SMS relay server
- Details
- Category: Raspberry
-
Also available:

- Hits: 2473
Unfortunately you need a USB A to USB A male cable which is very unusual. But there's a trick: Remove the lower part of the case which includes the SSD and pug in the USB bridge of the Argon case. Now you can use a commonly used USB extension cable to connect the SDD to your PC. Now use any common methods to install an OS on your SSD.
- Details
- Category: Raspberry
-
Also available:

- Hits: 20562
Owncloud has a very poor performance on Raspberry Pi. But seafile runs very fast if running on nginx. There exist already a lot of instructions how to install seafile on raspberry so you will find links to these website on the following page which I used to install seafile. In addition I wrote down the sequence of steps I executed. It's primaily a combination of the various installation instructions which I found. My config files of seafile running with nginx can be downloaded as sample config files for your convenience. In addition there is a startscript for /etc/init.d available which starts seafile all the time when Linux ist started and and stops it when it's shut down.
Characteristics of the seafileserver: foo.no-ip.org is used as external dns name, nginx (no apache), runs on secure https port and offers webdav services.
Read more: How to install seafile on Raspberry Pi ? (With config files)
- Details
- Category: Raspberry
- Hits: 14894
I backup my xbmc config on my raspberry pi with Linux and rsync.
On windows it's unfortunately not that easy. That's why I describe in the following paragraph how to create a backup on windows and how to restore a previous backup. In addition I provide two windows cmd files which execute the commands in sequence and make the backup and restore much easier. Three tools are requiered on windows: putty, pscp und plink which can be downloaded from the putty page. If you kick off the backup command with the at command on windows you will have an actual backup all the time.
- Details
- Category: Raspberry
-
Also available:

- Hits: 7561
We now have a new Raspberry4 gibt, which in contrast to the previous versions becomes quite hot. So everybody is interested in the effectiveness of either passive or active cooling and whether this cooling suppresses CPU throtteling.
I wrote a small script check_throttled.sh which reads the current throttling states of the Raspberry with vcgencmd get_throttled and if throtteling happens or already happend the meaning of the throttling bits is reported.
- Details
- Category: Raspberry
- Hits: 19331
Everybody running a server on a Raspberry with an open internet connection should protect against unauthorized access. There are various ways to protect. An additional protection is to restrict access to the Raspberry to specific IP ranges. The easiest way to do this is by using geoip and iptables and allow access from IPs from your country only. Actually this makes sense only if the server is used by you only and is no open server for everybody (owncloud, seafile, ...).
Execute following steps in order to install geoip on Raspbian Buster
Buster now uses nsf instead of iptables and requires a different format of the geoip files.
1) install xtables-addon
sudo apt install xtables-addons-common libnet-cidr-lite-perl libtext-csv-xs-perl libgeoip2-perl
2) Enable xt_geoip
sudo modprobe xt_geoip
echo "xt_geoip" | sudo tee -a /etc/modules-load.d/modules.conf
3) Download geoip files
mkdir /tmp/geoip
cd /tmp/geoip
/usr/lib/xtables-addons/xt_geoip_dl
4) Build geoip database now
mkdir -P /usr/share/xt_geoip
cd GeoLite2-Country-CSV_20190709
sudo /usr/lib/xtables-addons/xt_geoip_build -D /usr/share/xt_geoip
5) Add iptables rules to accept IPs from US and Germany
Example:
iptables -A INPUT -m geoip --src-cc DE,US -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -j ACCEPT6) Create following script to update your geoip database on a regular base
#!/bin/bash
geotmpdir=$(mktemp -d)
OLDPWD="${PWD}"
cd "${geotmpdir}"
/usr/lib/xtables-addons/xt_geoip_dl
dir="$(ls)"
cd $dir
/usr/lib/xtables-addons/xt_geoip_build -D /usr/share/xt_geoip
cd "${OLDPWD}"
rm -r "${geotmpdir}"
Execute following steps in order to install geoip on Raspbian Stretch
1) Install the xtables-addons
sudo apt-get install raspberrypi-kernel-headers
wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/xtables-addons/Xtables-addons/xtables-addons-2.14.tar.xz
tar xf xtables-addons-2.14.tar.xz
cd xtables-addons-2.14
./configure
make
make install
or
Kudos to @Basti
You can also use DKMS to build this module. Place source to /usr/src/xtables-addons-2.14 for example and create a dkms.conf in there. I have used the file shipped with xtables-addons-dkms_2.12-0.1_all.deb and edit the PACKAGE_VERSION="2.14" and
DEST_MODULE_LOCATION[0]="/extra". More infos about dkms (https://wiki.ubuntuusers.de/DKMS/).
2) Create a file /usr/local/bin/installGeoIP.sh and insert following code
#!/bin/bash
set -euo pipefail
set +e
if ! dpkg -l xtables-addons-common >/dev/null ; then
apt install xtables-addons-common
fi
if ! dpkg -l libtext-csv-xs-perl >/dev/null ; then
apt install libtext-csv-xs-perl
fi
set -e
if [ ! -d /usr/share/xt_geoip ]; then
mkdir /usr/share/xt_geoip
fi
geotmpdir=$(mktemp -d)
csv_files="${geotmpdir}/GeoIPCountryWhois.csv ${geotmpdir}/GeoIPv6.csv"
OLDPWD="${PWD}"
cd "${geotmpdir}"
/usr/lib/xtables-addons/xt_geoip_dl
/usr/lib/xtables-addons/xt_geoip_build -D /usr/share/xt_geoip ${csv_files}
cd "${OLDPWD}"
rm -r "${geotmpdir}"
exit 03) Make this file executable and invoke it
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/installGeoIP.sh
installGeoIP.sh
4) Add iptables rules to accept IPs from US and Germany
Example:
iptables -A INPUT -m geoip --src-cc DE,US -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -j ACCEPTIssues
If you get iptables: No chain/target/match by that name. error messages test whether the xtables_addons are installed correctly
modprobe -c | grep x_tab
should display a long list of modules.
modprobe xt_geoip
Should succeed.
depmod -a
may also help to fix the issue.
References
Linoxide: Block IP from countries using Geoip
Linxu headers rpi from mhieenka
Solved: iptables & geoip
Alternative: ipset usage (German)
Reddit: Firewall with geoIP capability on Debian 10
asds
Subcategories
Page 1 of 6


